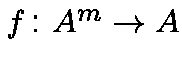 is the Hamming distance between
is the Hamming distance between
Letbe a finite ring. The non-linearity of
is the Hamming distance between
and the space of affine functions.
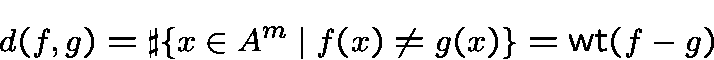
This notion applies in cryptography specially whenis the field of order
. The non-linearity of a boolean function
is given by
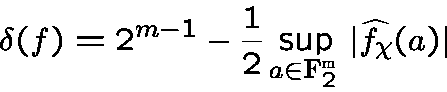
whereis the non-trivial character of
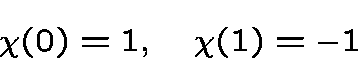
andis a Fourier coefficient of
.
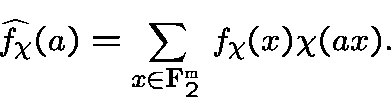
One defines the spectral amplitude of
and the spectral radius of order
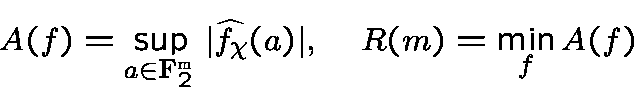
a boolean functionsuch that
is called highly non-linear.
What is the value of
?
Structure of highly non-linear functions ?